Polyamine boiler treatment technology a discussion in question & answer format
what is “polyamine” technology?
Polyamine is a term commonly used in the technical and commercial literature to describe both a relatively new class of boiler treatment technology, as well as one of the key active components in the program, spe- cifically a multifunctional, volatile, organic amine cor- rosion inhibitor.
As a boiler treatment, a Polyamine program is de- signed to provide protection against metallic corrosion throughout the boiler system, including the feedwater, boiler and steam condensate surfaces when fed at a single point in the system, normally to the boiler feed- water in the deaerator storage section.
what are the benefits of using a polyamine program?
The benefits of using a polyamine program include:
Simplicity – Complete system coverage and distribu- tion from a single liquid treatment fed at a single feed point.
This includes system-wide protection against both dissolved oxygen and acidic corrosion from the blend of volatile corrosion inhibitors without the feed of multiple products.
Polyamine products are designed to be used in combination with standard internal boiler treat- ments, including polymeric dispersants, phos- phates, and combination products.
Convenience – Program simplification in that two, or in some cases, three, separate products can be re- placed by a single Polyamine product.
Simplified, lower-cost single product feed system
Reduced chemical inventory and handling

Polyamine can handle stressed conditions – Water beads on low carbon steel test coupons exposed for seven days to 10 ppm of polyamine product, 100 ppb of dissolved O2 and 110°C (230°F) in deionized water. The average cor- rosion rate measured for them was 0.23 mpy (0.0060 mm/y).
Dependability & Assurance
Polyamine technology reduces the potential for both dissolved oxygen and carbonic acid corro- sion failures in the boiler feedwater and steam condensate systems. Our research has demon- strated that the Polyamine’s dual mechanisms of surface adsorption and neutralization of acid- ic contaminants provides highly effective protec- tion of metal surfaces throughout the steam generating system.
Reduced Total Cost of Ownership
While treatment cost benefits are very system- specific, a Polyamine program can often reduce overall treatment costs by eliminating the need to feed, inventory and monitor separate oxygen scavenger and neutralizing amine products.
The basis for cost savings is very simple – Poly- amine technology is designed to replace both the oxygen scavenger and neutralizing amine products in the majority of applications. In many cases, overall boiler treatment costs versus competitive programs can be reduced by 10 to 20%.
A significant aspect of the cost reduction equation is the efficient recycle of both the Polyamine and neutralizing amine corrosion inhibitors with the steam condensate when that stream is returned as boiler feedwater. Many dissolved oxygen scav- engers, such as sodium sulfite, are entirely non- volatile. Thus, they provide no protection of the steam condensate surfaces, and are lost entirely to the boiler blowdown.
how does it work?
The basic program consists of the multifunctional or- ganic amine corrosion inhibitor – the Polyamine – in combination with a specific blend of volatile organic neutralizing amines. The primary function of the Poly- amine component is to adsorb at the metal or metal oxide surface, restricting the access of aggressive species such as dissolved oxygen, carbonic acid, chlo- ride and sulfate anions, to the metal surface. The vol- atile neutralizing amines in the Polyamine treatment perform their normal function, neutralizing acidic con- taminants, and elevating the pH into the alkaline range, where the protective metal oxides are most stable and adherent.
Thus, a Polyamine program can provide “dual protec- tion” against both dissolved oxygen and low pH (acidic or carbonic acid) corrosion with feed of single product to a single feed point in the boiler feedwater circuit. This offers the potential for program simplification, reduction in traditional chemical inventories, and in many instances, improved economics.
Second, and very importantly, most filming amines, as well as non-amine filming corrosion inhibitors, are not appreciably volatile under boiler conditions. If fed to the deaerator, feedwater system or boiler itself, the filming inhibitor will not leave the boiler in measurable quantities, and thus will not provide protection of the steam condensate circuit. This limitation may be overcome by feeding the product directly to the steam header, but it is sometimes difficult to find a suitable injection point in complex, multiple boiler systems that ensure even distribution of the treatment and effective, full system coverage. In addition, this limitation may require that multiple products be fed to several points in the feedwater and steam condensate sys- tem to achieve effective coverage and corrosion pro- tection of the entire system.
Unlike conventional filming inhibitor technology, the Polyamine is significantly volatile under the full range of boiler pressures, and when added to the feedwater, it will readily enter the steam phase, even at pressures below 100 psig (< 7 barg), provid- ing effective corrosion protection in combination with the program’s neutralizing amine components to the entire steam condensate system. In addition, uniform levels of Polyamine will reach all points in the steam system based on the distribution and mix- ing that occurs in the boiler.
will the polyamine program provide protection against dissolved oxygen corrosion in the absence of oxygen scavenger?
Yes. Polyamine technology will provide very effec- tive protection against dissolved oxygen corrosion in boiler systems equipped with an efficient thermal deaerator, which may also be referred to as a pres- sure deaerator. Thermal deaerators are typically rated to produce effluent dissolved oxygen levels below 10 ppb (µg/l) as O2 when operated according to manufacturer’s specifications and design limits. However, our experience has demonstrated that the expected range of performance of deaerators in in- dustrial and commercial boilers in the absence of an oxygen scavenger is typically between approximately 5 and 40 ppb as O2. We have found that a Polyamine program produced superior corrosion control even at these higher levels of dissolved oxygen. It is im- portant to emphasize that Polyamine technology is not recommended for application in systems which are not equipped with a thermal (or pressure) de- aerator.

can a polyamine program be fed to a system with a superheater and steam turbine?
Yes, Polyamine chemistry has been successfully ap- plied in systems with superheaters and steam tur- bines.
will the polyamine chemistry impact condensate polisher resin performance or operation?
No. Our testing has indicated there was no loss in ca- pacity or performance of standard cationic condensate polisher resins exposed to Polyamine treatment.
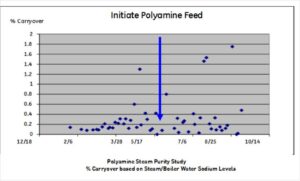
will the polyamine impact steam purity or increase carryover?
No. The Polyamine chemistry was evaluated based on steam sodium measurements in our Research-scale test boilers at pressures between 7 barg (100 psig) and
100 barg (1500 psig), as well as in a long-term test in an operating watertube boiler (see Figure 2 below). There was no measurable impact on steam purity, nor any operational issues associated with moisture carryover or foaming.
will a polyamine program impact steam cation conductivity?
In that the Polyamine products contain organic amine compounds, a slight but measurable increase in cation conductivity would be expected in high- pressure systems. This would be comparable to the effect observed with our standard neutralizing amine products.
will the polyamine replace my current boiler internal treatment/ deposit control program?
No. The Polyamine treatment is primarily designed for corrosion control, and does not directly replace the functionality of our internal treatment programs.
As discussed above, the Polyamine treatment may re- place the dissolved oxygen scavenger and neutralizing amine products in boiler systems with efficient ther- mal deaerators.
with what internal treatment programs is the polyamine compatible?
Based on extensive testing, our Polyamine treatments do not negatively impact the effectiveness of our de- posit control chemistries, including polymer, chelant and phosphate-based treatments.
will the polyamine treatment impact a coordinated or alkaline phosphate-ph control program?
Our Polyamine products contain a low volatility amine component that will function as a pH buffer in the boil- er, and which can serve as the basis of an All-Volatile Treatment (AVT) program. In high-pressure boilers utilizing some form of phosphate-pH control, such as coordinated PO4-pH, this amine could elevate the boil- er water pH independently of the phosphate product, and this should be considered in designing the pro- gram, specifically the PO4-pH control range.
is the polyamine chemistry compatible with all- volatile treatment (AVT) control?
Yes. The Polyamine product can serve as a single- product AVT program by virtue of the combination of the volatile Polyamine corrosion inhibitor and specific blend of high-performance neutralizing amines. It will provide superior pH elevation and balance in the feed- water, boiler circuits and steam condensate versus ammonia treatment, especially in areas of two-phase (steam-liquid) flow.
The low volatility amine component also provides en- hanced corrosion protection, along with the Polyam- ine, in the presence of aggressive contaminants, such as chloride, especially in areas of potential concentra- tion, such as under porous deposits at boiling heat transfer surfaces.
The Polyamine treatment also includes a high vola- tility neutralizing amine component that provides effective corrosion protection of complex steam condensate systems.
is there a polyamine test?
Yes. There is a wet photometric field method for the DR-series photometers. The method is named for the two active polyamine products, Steamate* PAS6071 and PAS6074, and is based on a set of Ben- gal Rose reagents, which together react with the Polyamine corrosion inhibitor to produce a pink col- oration. The intensity (absorbance) of the pink com- plex is measured at 560 nanometers, and is directly proportional to the level of Polyamine active in the sample. The results are expressed as ppm product, for example, ppm as Steamate PAS6074. The Rose Bengal Test is specific for the Polyamine chemistry, and the result does not reflect the neutralizing amine components of the product.
Measurement in the Boiler feed water and steam condensate allows verification of the presence of the Polyamine inhibitor. Please consult the Polyamine Field Analytical Procedure sheets for specifics on the field test method.
where can I learn more about VEOLIApolyamine boiler treatment technology?
Contact your local VEOLIArepresentative. You can find a contact near you by visiting www.veoliawatertechnologies.com and clicking on “Contact Us”.



